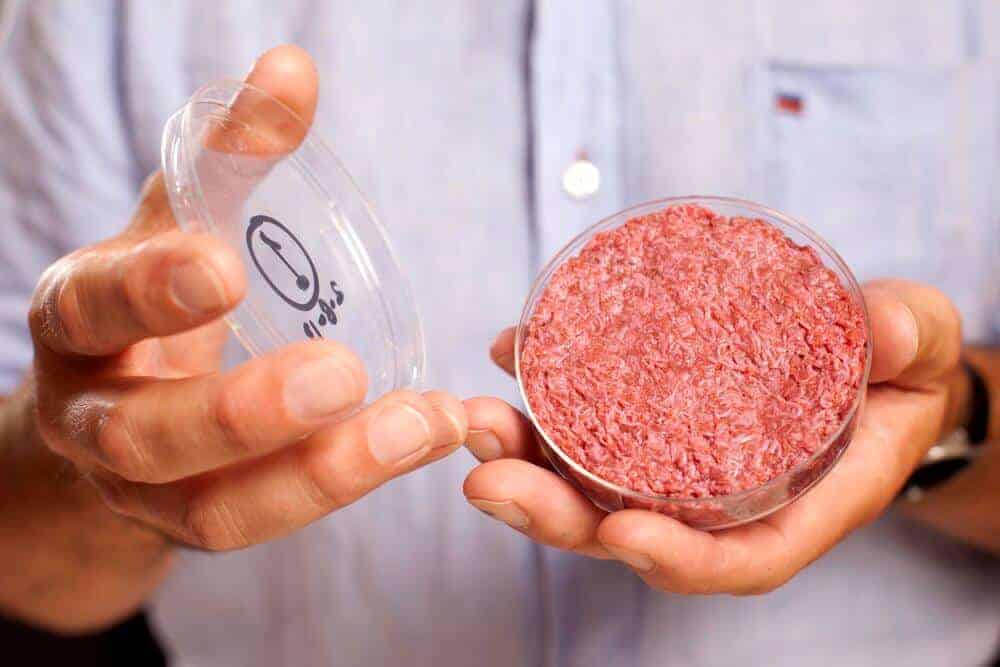
When the world’s first cellular burger was publicly presented in December, 2013, the idea of cultivating meat in a laboratory was shrug off as pure science fiction. Seven years later, the vision of cultured meat has become reality: Chicken nuggets from cultured meat are now being served in a restaurant in Singapore since December 2020.
Cultured meat heralds a paradigm shift in the production of meat as it is manufactured by in-vitro cultivation of animal cells. In doing so, cultured meat breaks with the logic of producing meat through livestock farming and animal slaughter.
New consumer preferences promote sustainable development
The idea of cultured meat hits the current zeitgeist. A growing number of people desire to consume in a more sustainable way and are therefore breaking with their traditional consumption patterns. This explains the recent meteoric rise of plant-based meat alternatives. The new generation of plant-based meat alternatives from companies like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods have successfully entered the mass market backed by a clever strategy: They target consumers who derive pleasure from eating meat, yet still wish to reduce their overall meat consumption. These changing consumer preferences open up new opportunities for a new form of nutrition with a very favorable outlook for sustainable consumption.
Cultured meat’s advantage for sustainable development: A product for all meat eaters
While plant-based meat alternatives imitate meat products, cultured meat is a perfect substitute for conventional meat. Ultimately, it will be impossible to distinguish cultured meat from its conventional counterpart: it smells, looks, and tastes the same. Contrary to plant-based meat alternatives, cultured meat does not target a specific customer group, but appeals to all meat consumers. This is precisely what gives rise to cultured meat’s immense opportunities for sustainable development.
Cultured meat: A great opportunity to contribute to sustainable development
Cultured meat has a high potential to substantially reduce the environmental footprint of the meat industry and thus, contribute to sustainable development. Studies predict that compared to conventional meat production, cultured meat will emit up to 90% less greenhouse gases. Thus, the market diffusion of cultured meat can make a significant contribution to the mitigation of global warming. Moreover, cultured meat holds the prospect to improve global food security as its production is independent from climate and land quality. Taken together, cultured meat has the power to initiate a transition in the meat industry and bring it on a more sustainable path. Therefore, companies that begin to explore cultured meat now make an important contribution to sustainable development.
About the author
As part of his research on the future of agriculture and nutrition, Prof. Dr. Nick Lin-Hi has already been dealing with cultured meat since several years. He is one of the leading experts for cultured meat in Germany and is regularly involved in discussions about its relevance with representatives from business and politics. As professor for business and ethics, he is researching and teaching at the University of Vechta and thus, in Germany’s hotspot of intensive animal farming. TV, radio, and various online and print media are regularly reporting about his work.
What is your stance on cultured meat? Share your perspective in our scientific survey. With just 8 minutes of your time, you can shape the public and scientific discussion about this innovation. For each of the first 300 completed surveys, we will donate 1€ to UNICEF. To take part, simply follow this link: